Soil and Groundwater Remediation | Services
Apply water technology to reveal the power of land

The Kurita Group provides inspection, remediation, and consultation regarding hazardous substances contamination of soil and groundwater, reducing environmental impact.
About soil and groundwater remediation
Soil and groundwater pollution is caused by hazardous substances leaking from factories and other sites, accumulating underground and spreading them into groundwater. This pollution causes not only obstacles but also leads to health hazard issues. The Kurita Group offers from inspection to remediation of soil and groundwater with consulting based on multiple technologies and abundant knowledge as a one-stop solution, contributing to solve issues and reduce environmental impact of customers.
Soil and groundwater survey
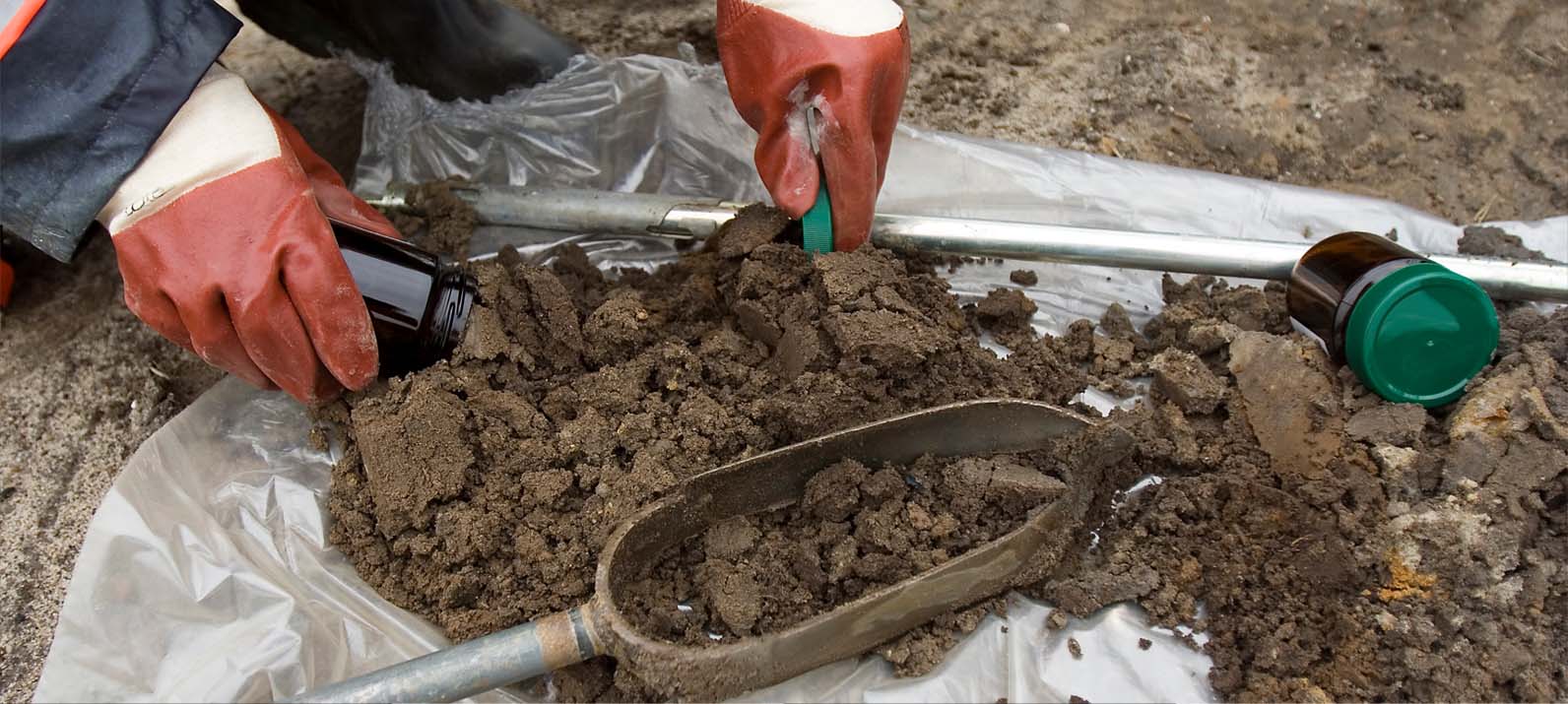
Kurita Group conducts geographical and historical ground survey, including materials gathering and interviews about the history of hazardous substance use and other matters, qualitatively evaluating the risk of soil and groundwater pollution. As a result of the survey, the evaluated land evaluated that has a risk pollution is then analysized to the deeper depth of its soil and groundwater to evaluate quantitively.

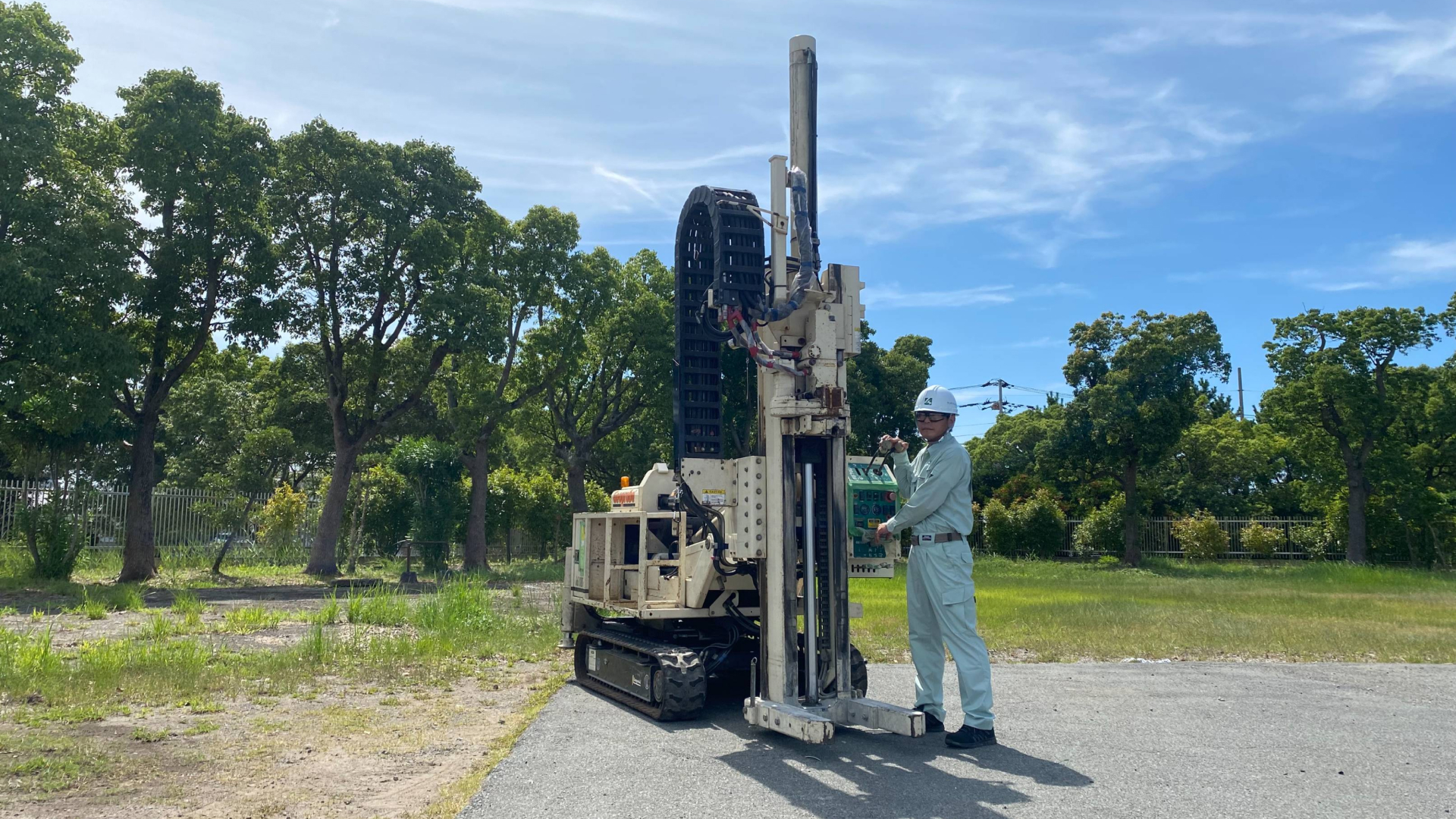
Accurate on-site survey of pollution sources
Challenges
The boring survey for VOCs stipulated in the Soil Contamination Countermeasures Act involves collecting soil samples at 1m depth intervals and analyzing them. However, soil contamination may locally exist between sampling depths, and an accurate understanding of the contamination situation is necessary to ensure reliable soil and groundwater remediation.
Solutions
The Kurita Group's pollution source exploration enables on-site, real-time monitoring of continuous data in the depth direction. By understanding the details of the contamination situation at the site and adding survey points as needed, it is possible to investigate and narrow the source of contamination efficiently. Accurate identification of the pollution source improves the reliability of soil and groundwater remediation, which will reduce environmental impact.
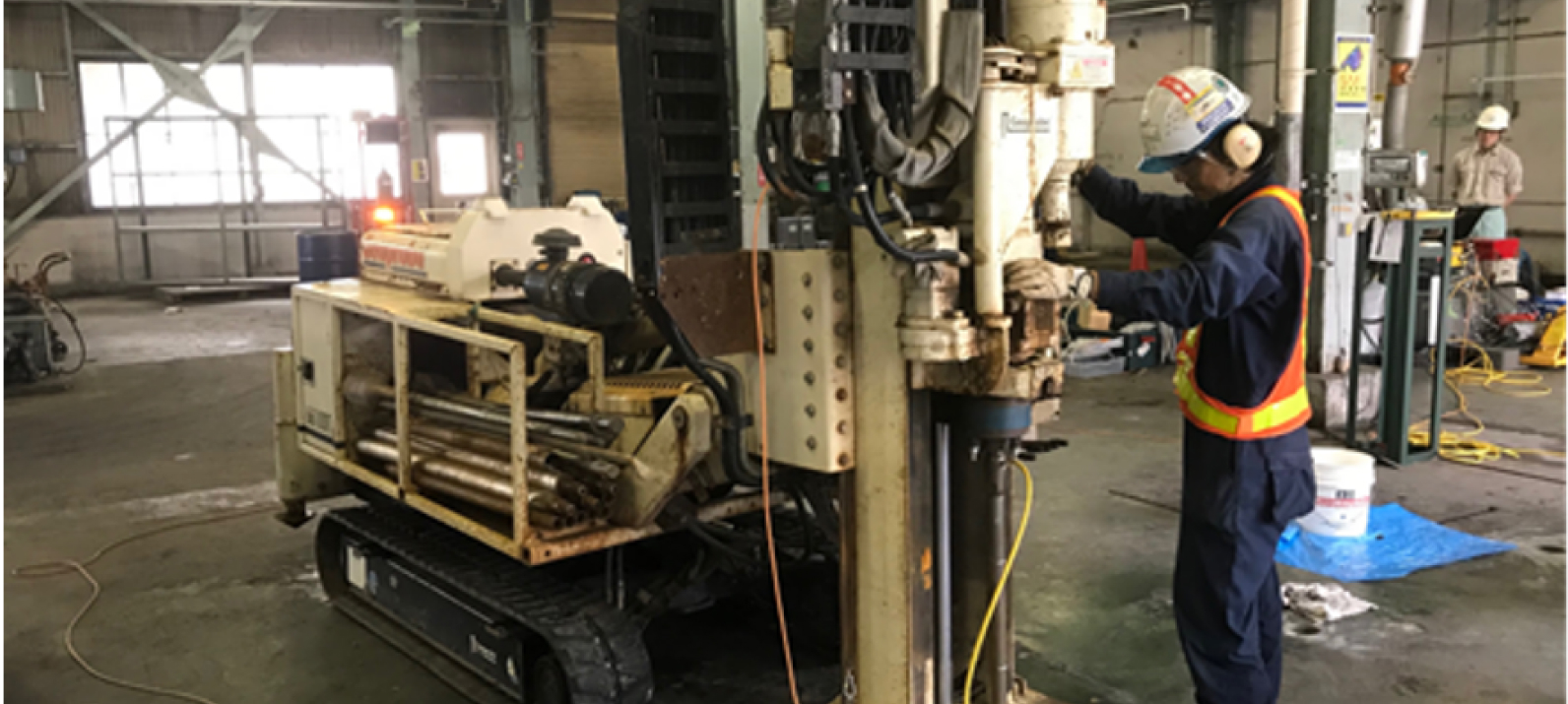

Reduction of environmental impact
In-situ remediation
In-situ purification is a method of purifying contaminated soil on-site without excavating, including breaking down VOCs by microbes and chemicals and physical removal by groundwater pumping or underground gas suction. Due to enabling the works without dismantling buildings, it can be applied at factories in operation.
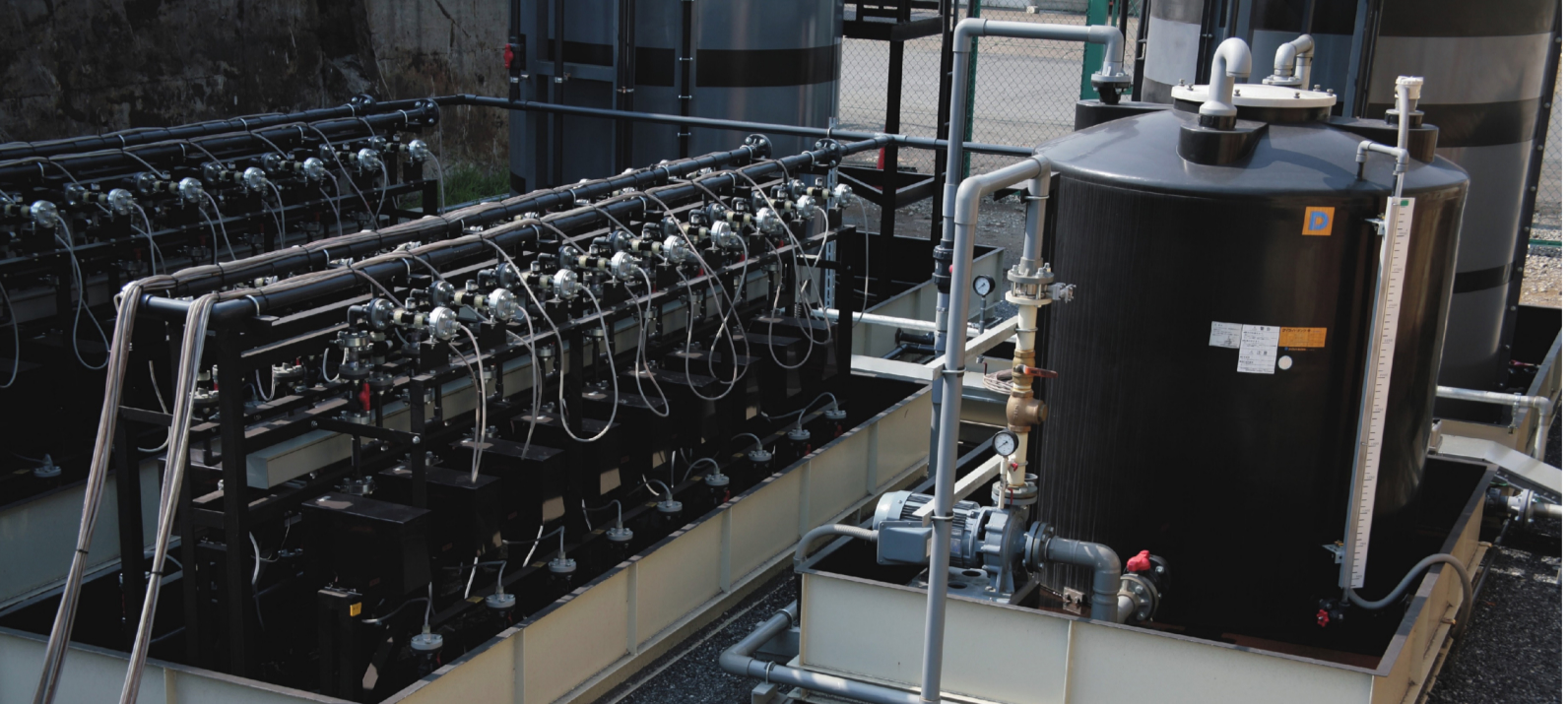

Reduce environmental impact and GHG emissions by reliable cleaning
Challenges
If there is existing soil or groundwater pollution under the building, it is difficult to dismantle the building while it is in operation. Therefore, rather than removing contaminated soil by excavation, in-situ purification in which microorganisms decompose VOCs is applied. If VOCs penetrate into layers where it is difficult for water to drain (low-permeability layer), they will be adsorbed by the soil. It is difficult to completely remediate that soil by bioremediation, and the remediation period is prolonged due to rebound.
Solutions
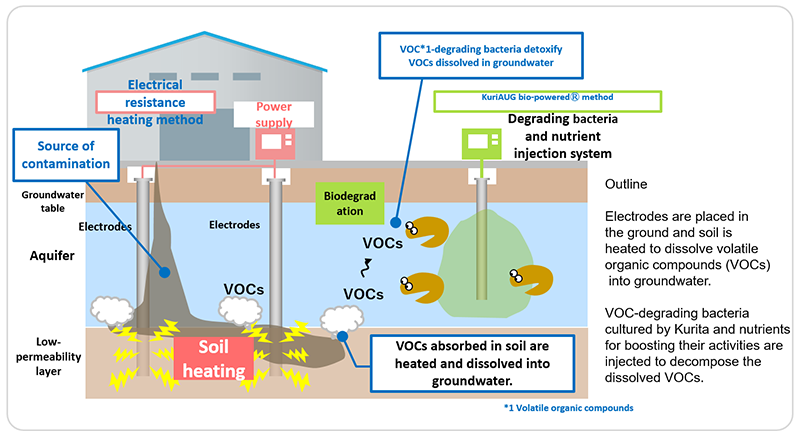
Power Bio E-PLUS™ can remediate VOCs contamination in the short term. It is a soil and groundwater remediation technology that combines the electrical resistance heating method, which elutes VOCs absorbed in the soil in the low-permeability layer into groundwater by electric current between electrodes placed in the ground. KuriAUG bio-powered™ method decomposes and detoxifies the VOCs dissolved in groundwater by the effect of microbial. This technology enables the removal of VOCs from soil in the low-permeability layer and suppresses rebound after remediation. In addition, enabling soil remediation without excavation can reduce GHG emissions compared with excavation-type remediation.