Offices and Commercial Facilities | Industries
Use water for steam and to create a comfortable space

To introduce the solutions for offices and commercial facilities.
Kurita Group solutions for offices and commercial facilities
With corporations trending toward a carbon-neutrality by 2050, energy conservation efforts in all industries and applications are accelerating. Large-scale buildings, such as offices, hotels, hospitals, and data centers, are also taking various measures to reduce power consumption to realize energy conservation. However, measures like replacing equipment and parts with high-efficiency and improving the heat and thermal insulation of buildings have largely been completed, so further energy-saving efforts are required. Additionally, health and safety must also be considered. In the heat exchangers of refrigeration equipment (open cooling towers), corrosion, scale, and biofouling can cause shutdowns of the cooling process and air conditioning equipment, shortened equipment life, and energy loss. The Kurita Group provides water treatment chemicals that eliminate these problems and prevent their occurrence and continued maintenance. We also use cooling water chemicals to inhibit the Legionella bacteria growth and sanitize cooling towers to maintain a hygienic facility environment.
Challenges and solutions for office and commercial facilities
01. To combine the visualization of refrigeration energy loss through LTD monitoring and the Kurita NA™ series, which inhibits damage and Legionella bacteria, enabling highly efficient operation of refrigeration equipment and then reducing electricity consumption and GHG emissions.
Challenges
The electricity used to air condition large buildings accounts for most of the electricity used in the entire building. While slime on cooling towers reduces the heat transfer coefficient and causes energy loss, it does not significantly interfere with operation. This type of energy loss is sometimes difficult to notice.
Solutions
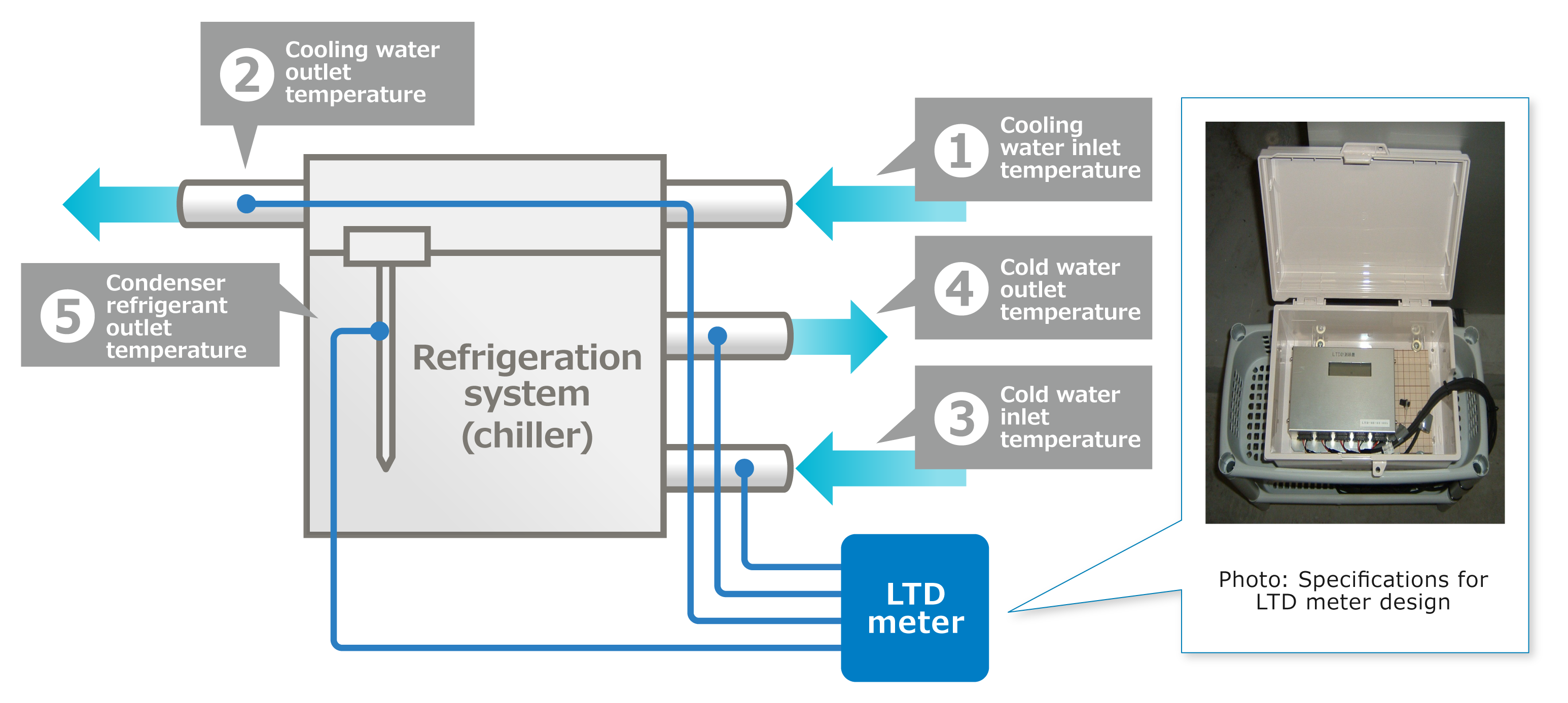
The heat transfer coefficient of the refrigeration equipment's heat exchanger is quantified by the leaving temperature difference (LTD), which measures the difference between the refrigerant outlet temperature and the cooling water outlet temperature. When slime or other contaminants adhere to the heat exchanger, the heat transfer coefficient decreases, leading to a larger temperature difference and an increase in the LTD. This value is continuously monitored to quantify energy losses and calculate the related GHG emissions, helping visualize the gap between actual performance and the customer's GHG reduction targets. Additionally to protecting assets and human health, Kurita's NA incorporates sensing technology that automatically controls the chemical injection volume using an LTD meter. This optimizes chemical usage, improving the operational efficiency of the refrigeration equipment, reducing electricity consumption, lowering GHG emissions, and ensuring a hygienic facility environment.